Introduction:
If you’ve ever wondered how the good guys (White hat hackers) on the internet go after the bad guys (Black hat hackers), one way is something called a Honeypot. You see, in addition to the security measures you might expect, such as strengthening a computer network to keep cybercriminals out, the good guys use a honeypot to do just the opposite — attract the bad guys.
Like mice to cheese-baited mousetraps, cybercriminals are attracted to honeypots — not because they’re honeypots. The bad guys think the honeypot is a legitimate target, something worthy of their time. That’s because the bait includes applications and data that simulate a real computer system.
What is Honeypot?
A Honeypot is a trap that an IT pro lays for a malicious hacker. It is an information resource whose value lies in unauthorized or illicit use of that resource. Honeypot is a computer or network resource that appears to be a part of the network, but have been deployed as a trap to attract hacker.
The principle behind it is simple: Don’t go looking for attackers. Prepare something that would attract their interest and then wait for the attackers to show up.
Honeypot Deployment:
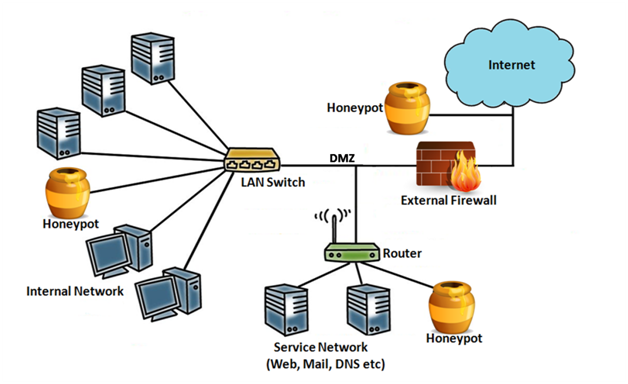
Honeypot can be deployed in a variety of locations in the network.
1) Outside the external firewall
– Does not increase the risk for internal network
– Since it attracts and traps attacks, it reduces the amount of traffic, particularly attack traffic to the firewall.
– So external honeypots reduce alerts reduced by firewall
– Cannot trap internal attackers
2) In DMZ (De – Militarized Zone)
– Used to trap attack to public facing service.
– The DMZ is not fully accessible.
– Usually firewall blocks the traffic to DMZ.
– So if firewall allows the traffic to the honeypot, this means that we are opening a firewall. This is a security risk.
3) In an internal network (alongside servers and workstations)
– It can catch internal attacks.
– It can also detect misconfiguration in the firewall.
– A compromised honeypot can attack other internal systems.
– The firewall must adjust its filtering to allow traffic to the internet. Security risk is involved.
CLASSIFICATION:
Honeypots can be broadly classified based on 2 main categories:
1) Level of Interaction
i. Low level of Interaction
ii. High level of Interaction
i. Low Level of Interaction:
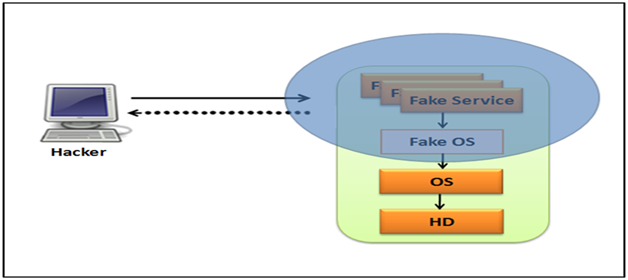
– These honeypots have limited interaction with the system; they work by imitating services and operating systems
– There is no operating system in place that an attacker can interact with.
– They capture and identify any traffic coming into the network. Also, new viruses and new worms are identifiable.
– Only one or a few simple services are available for the attacker to interact with. Hence secured.
– All communication attempts with any particular functions such as a web server are logged and investigated afterwards.
– Help network administrator to monitor any attempts of attacks on the system in a passive manner.
– Example – Most used example is Honeyd
Working of Honeyd
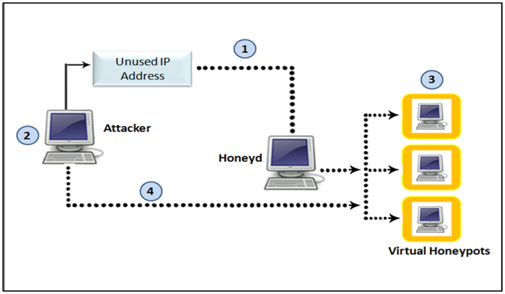 – Honeyd monitors unused IP space.
– Honeyd monitors unused IP space.
– When an attacker probes an unused IP, Honeyd detects the probe, takes over that IP via ARP spoofing, then creates a virtual honeypot for the attacker to interact with (Honeyd can create multiple virtual honeypots to fool attackers on all unused addresses). The attacker is fooled into thinking he is interacting with a successful hacked system.
– Besides, Honeyd automatically updates its list of unused IPs as Systems are added or removed from the network.
ii. High Level of Interaction:
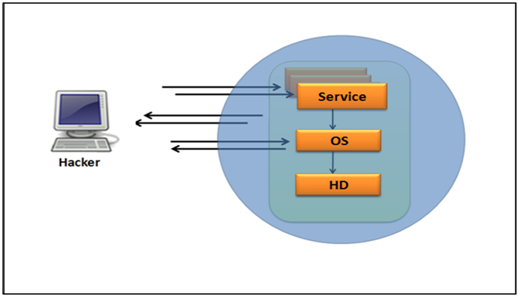
– Complex solutions – involve real operating systems and applications.
– Nothing is emulated, the attackers are given the real thing
– Can be compromised completely, allowing an attacker to gain full access to the system and use it to launch further network attacks
– Example – Honeynet
Working of Honeynet
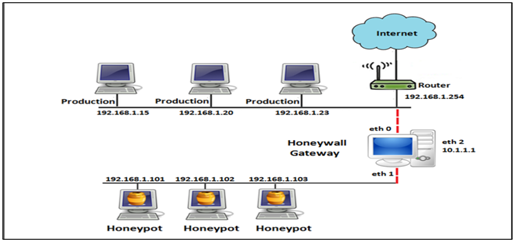
Honeynet is a group of Honeypots in a network and has 3 components:
1. Data capture:
Honeynets are architecture, an entire network of computers designed to attack. The idea is to have an architecture that creates a highly controlled network, one where all activity is controlled and captured. Within this network we place our intended victims, real computers running real applications.
2. Data control:
The Honeynet controls the attacker’s activity. Honeynets do this using a Honeywall gateway. This gateway allows inbound traffic to the victim systems but controls the outbound traffic using intrusion prevention technologies.
3. Data analysis:
The data is analyzed and monitored by the system admin.
2) Purpose
I. Production Honeypot
– Used to reduce risks in a business/production environment.
– Easy to use, capture only limited information, Low-level interaction
II. Research Honeypot
– Gather as much information as possible
– Complex to deploy and maintain, capture extensive information, and are used primarily by research, military, or government organizations
– Collect compact amounts of high-value information
– Discover new Tools and Tactics
– Understand Motives, Behavior
– Develop Analysis and Forensic Skills
Honeytokens
– Bogus or dummy IT resources which are created or placed in the system
Types of Honeytokens:
– Fake Email Addresses
Set up Bogus email accounts not actually connected to the enterprise, and left inactive but visible to mail server.
– Fake Database Data
Inserting fake records into an existing database
Advantages of Honeypot
I. Small datasets of high value
Honeypots collect in-depth information. Instead of logging on 1 GB of data a day they can log only on 1 MB of data a day. Instead of generating 10,000 alerts a day they can generate only 10 alerts a day.
II. New tools and tactics
Honeypots are designed to capture anything thrown at them including tools and tactics never seen before.
III. Encryption or IPv6
Unlike other security technologies honeypot works fine in encrypted or IPv6 environments. It does not matter what the bad guys throw at honeypot, honeypot will detect and capture it.
IV. Simplicity
Honeypots are conceptually very simple. No fancy algorithms to develop, state tables to maintain or signatures to maintain.
Disadvantages of Honeypot
I. Time Consuming
Building, configuring, deploying and maintaining honeypot is time-consuming.
II. Limited View
It only captures activity from the system which has got honeypot installed in it and not other systems on the network.
III. Distinguishable
It is easy for an experienced hacker to understand if he is attacking a honeypot system or a real system.
Conclusion
– Honeypot helps you to know your enemy.
– Honeypots have their advantages and disadvantages: No Security system can guarantee you 100% security. So they should be used with other security measures.
– A useful tool for trapping attackers, capturing information
– Analysis of attacker activities can be done
– Needs proper planning – without enough planning and consideration may introduce more risk to an existing network.
References
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Honeypot_(computing)
http://www.iraj.in/journal/journal_file/journal_pdf/3-174-143867333032-40.pdf
https://searchsecurity.techtarget.com/definition/honey-pot