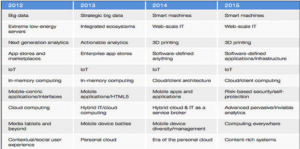
Information Technology is the study, design, development, application, implementation, support or management of computer-based information systems. The Latest Trend of Information Technologies are: Cloud Computing, Internet of Things (IoT), Big data, Cyber security, Context-Rich Systems, Increased automation, Continued mobile pervasiveness, Web-Scale IT, 3D Printing.
Top 9 emerging technologies
1. Cloud Computing
The practice of using a network of remote servers hosted on the Internet to store, manage, and process data. Cloud computing offers 3 types of broad services mainly Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS) and Software as a Service (SaaS)
Some of the advantages of Cloud computing are it reduces IT infrastructure cost of the company, promotes the concept of visualization,which enables server and storage device to be utilized across organization. Cloud computing makes maintenance of software and hardware easier as installation is not required on each end user’s computer. Cloud is the new style of elastically scalable, self-service computing, and both internal applications and external applications will be built on this new style. While network and bandwidth costs may continue to favor apps that use the intelligence and storage of the client device effectively, coordination and management will be based in the cloud.” Disadvantages of Cloud computing are issues concerning privacy, compliance, security, legal, abuse, IT governance.
Cloud computing is becoming the hub for operational infrastructure. Big data, generated through IoT, is an important driver for organizations to move to the cloud.The reason behind the movement to cloud-based operations are numerous, from IT agility to IT innovation and employee collaboration. Technologies such as software-defined networking (SDN) and network functions visualization (NFV) are being looked into to give greater agility to cloud investments.
2. The Internet of Things (IoT)
Rapid increase in IoT solutions being deployed to advance business intelligence. ABI Research reported a 20% increase in IoT connected devices in 2014 from 2013. This year, Cisco predicts there will be 25 billion connected devices, which will double to 50 billion by 2020. Information Age suggests IoT will revolutionise business by allowing companies to improve value propositions, engage with customers on levels previously unavailable and build entirely new revenue streams.
Investment in IoT has mainly come from the IT and telecoms industry, which will naturally benefit from the increase in data generated and application capabilities for mobile devices. In 2015, spectators predict investment in IoT will increase outside this industry. The retail industry is one sector in particular that is looking to tap into sensor data generated via wearable technology to provide highly targeted products and services to their customers. As businesses look to IoT technologies to provide more insight, there is an ever-increasing demand for analysts capable of transforming IoT data into actionable business intelligence. IoT will become the next critical focus for data and analytics services with IDC predicting 30% CAGR over the next five years.
3. Big data
Big data as a concept is ever evolving as the capacity to mine structured, semi structured and unstructured data increases. In 2014, organizations were making more informed business decisions and becoming more intelligent as they interact with their customers. More sophisticated ‘recommendation engines’ anticipating users’ interests more accurately for services such as Netflix, Amazon and Google. Further, credit reference agencies have been using big data to inform on lending decisions by developing the algorithms used to generate credit ratings. Retail, logistics and budget planning have all seen significant advancement last year due to greater business intelligence.
The increasing influx of data available to organizations will require the infrastructure being used to house, process, analyze and visualize intelligence to expand. The IDC predicts that rich media analytics will be the driver behind many big data projects, expecting this area to at least triple in size.The increased demand for greater sophistication in analysis and data consumption will require organizations to refine talent acquisition strategies to compete in the skills gap.
4.Cyber security
IT security is an obvious priority in an environment infested by spam, bugs, bots, browser holes, exploits, spyware, adware, denial of service (DoS) attacks, viruses and phishing. IT security breaches are serious business problems that can often result in significant financial loss and collateral damage. Organizations need to be proactive in protecSecurity weaknesses have been marked down to a number of key areas such as mis-configuration issues, third party providers, lack of network diversity and most worrying of all, lack of qualified security talent.
The cyber security skills gap is perhaps the underlying issues having a knock-on effect on industry and the economy. Cyber security skills are a global priority but, with a lack of consistency in accepted career definitions, organizations are experiencing difficulties in attracting new talent and progressing existing professionals. To offset the skills deficit, talent from the ‘gaming’ industry are being brought into the security sphere and their skills adapted for this arena.
The information security industry has an opportunity to re-define itself and build on the negative global coverage it observed last year to attract new talent. The Internet Systems Security Association (ISSA) identified the need for an internationally accepted framework that would define the cyber security career for individuals in the profession. To attract new entrants and so that pros can advance in their career, ISSA have developed the Cybersecurity Career Lifecycle (CSCL). This pro-active approach to industry development could go a long way to help fill the estimated 300,000 to 1,000,000, and rising, currently vacant global cyber security positions.
All roads to the digital future lead through security. However, in a digital business world, security cannot be a roadblock that stops all progress. Organizations will increasingly recognize that it is not possible to provide a 100 percent secured environment. Once organizations acknowledge that, they can begin to apply more-sophisticated risk assessment and mitigation tools. On the technical side, recognition that perimeter defense is inadequate and applications need to take a more active role in security gives rise to a new multifaceted approach. Security-aware application design, dynamic and static application security testing, and runtime application self-protection combined with active context-aware and adaptive access controls are all needed in today’s dangerous digital world. This will lead to new models of building security directly into applications. Perimeters and firewalls are no longer enough; every app needs to be self-aware and self-protecting.
5. Increased automation.
There is no escape that people costs continue to be a big part of total IT costs. The use of cloud services will continue to reduce this (with cloud service providers achieving lower costs through both economies of scale and the use of automation) but there is still a need to reduce human touch points, and the associated costs, within corporate data centers and operational environments – with speedier delivery and fewer human errors secondary benefits. 2015 will see even greater automation adoption by corporate IT organizations under pressure to reduce costs and better demonstrate business value.
6. Continued mobile pervasiveness
Continued improvements in anytime, anywhere, any device access to data and services will continue to drive the need for better mobile apps and experiences, and the use of personal devices for work purposes. Not only will this dictate the need for better service and app design and delivery, and more intelligent approaches to BYOD, but also the need to consider the security implications of mobility such as data segregation issues – with personal and business data and applications isolated from each other on the same device.
7. Context-Rich Systems
Ubiquitous embedded intelligence combined with pervasive analytics will drive the development of systems that are alert to their surroundings and able to respond appropriately. Context-aware security is an early application of this new capability, but others will emerge. By understanding the context of a user request, applications can not only adjust their security response but also adjust how information is delivered to the user, greatly simplifying an increasingly complex computing world.
8. Web-Scale IT
Web-scale IT is a pattern of global-class computing that delivers the capabilities of large cloud service providers within an enterprise IT setting. More organizations will begin thinking, acting and building applications and infrastructure like Web giants such as Amazon, Google and Facebook. Web-scale IT does not happen immediately, but will evolve over time as commercial hardware platforms embrace the new models and cloud-optimized and software-defined approaches reach mainstream. The first step toward the Web-scale IT future for many organizations should be DevOps — bringing development and operations together in a coordinated way to drive rapid, continuous incremental development of applications and services.
9. 3D Printing
Worldwide shipments of 3D printers are expected to grow 98 percent in 2015, followed by a doubling of unit shipments in 2016. 3D printing will reach a tipping point over the next three years as the market for relatively low-cost 3D printing devices continues to grow rapidly and industrial use expands significantly. New industrial, biomedical and consumer applications will continue to demonstrate that 3D printing is a real, viable and cost-effective means to reduce costs through improved designs, streamlined prototyping and short-run manufacturing.
Reference
1] http://certification.about.com/od/certifications/a/IT_trends_3.htm
2] http://www.information-age.com/it-management/strategy-and-innovation/123458793/2015s-most-critical-information-technology-trends#sthash.
3] http://certification.about.com/od/certifications/a/IT_trends.htm?utm_term=Current%20Trends%20in%20Information%20Technology&utm_content=p1-main-3-title&utm_medium=sem-rel&utm_source=google&utm_campaign=adid-0700b17f-3b7a-44a8-a19f-aa0563c92bb0-0-ab_gsb_ocode-22855&ad=semD&an=google_s&am=broad&q=Current%20Trends%20in%20Information%20Technology&dqi=&o=22855&l=sem&qsrc=6&askid=0700b17f-3b7a-44a8-a19f-aa0563c92bb0-0-ab_gsb