Biometric refers to recognizing a person based on one or more behavioral characteristics. It involves scanning of biological inputs or the analysis of any part of the human body for identification and access control. It is also used to identify individuals in groups that are under surveillance.
Biometric authentication technology is used to protect different kinds of systems – from a reasoning system to a digital system like computers, mobile phones, laptops and other password protected software’s and sites to a physical system protected by physical barriers, such as research labs, banks etc.
This technology uses a biometric device, which is a security identification and authentication device. These devices are automated to verify and recognize the identity of a living person based on a physiological or behavioral characteristic. Physiological characteristics includes, but are not limited to fingerprints, facial images, iris and retina recognition, voice recognition, palm veins, palm print, hand geometry and in some cases even DNA and odor/scent. Behavioral characteristics are related to the behavior of a person, which includes typing rhythm and voice.
5 most popular Biometric Authentication systems
- Facial recognition systems: It is one of the most flexible biometric identification methods which can work even when the subject is not aware of being scanned. It works with numeric codes called face prints, which identify 80 nodal points on a human face.
-

Face recognition 2. Finger scanning: It’s potential to identify people based on a near-universal physical trait. The advancement of this technology has led to the development of fingerprint recognition systems which are small and inexpensive. Typical examples are mobile phones and laptops, building and car doors, border control and other high security military applications.
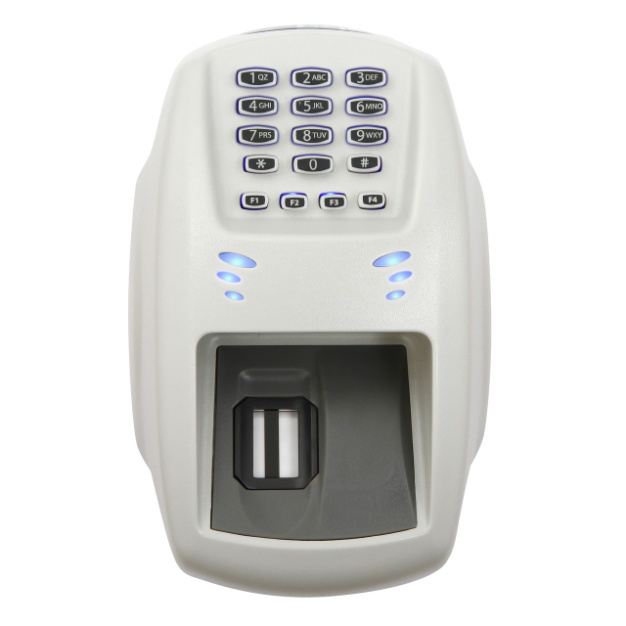

Biometrics device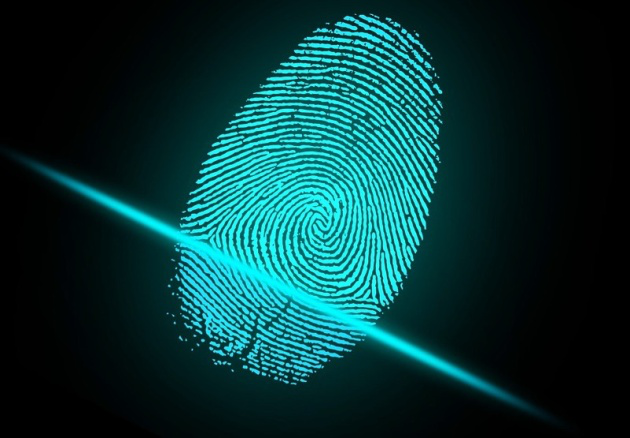 
Finger print - Iris recognition: It uses pattern recognition techniques based on high-resolution images of the irises of an individual’s eye. Iris recognition utilizes the same technology as cameras coupled with subtle infrared illumination to reduce the specular reflection from the convex cornea. This creates detailed and rich images of the complicated structures of the iris. The images are converted and stored as digital templates which provide a mathematical representation of the iris that enables unique positive identification of individuals.
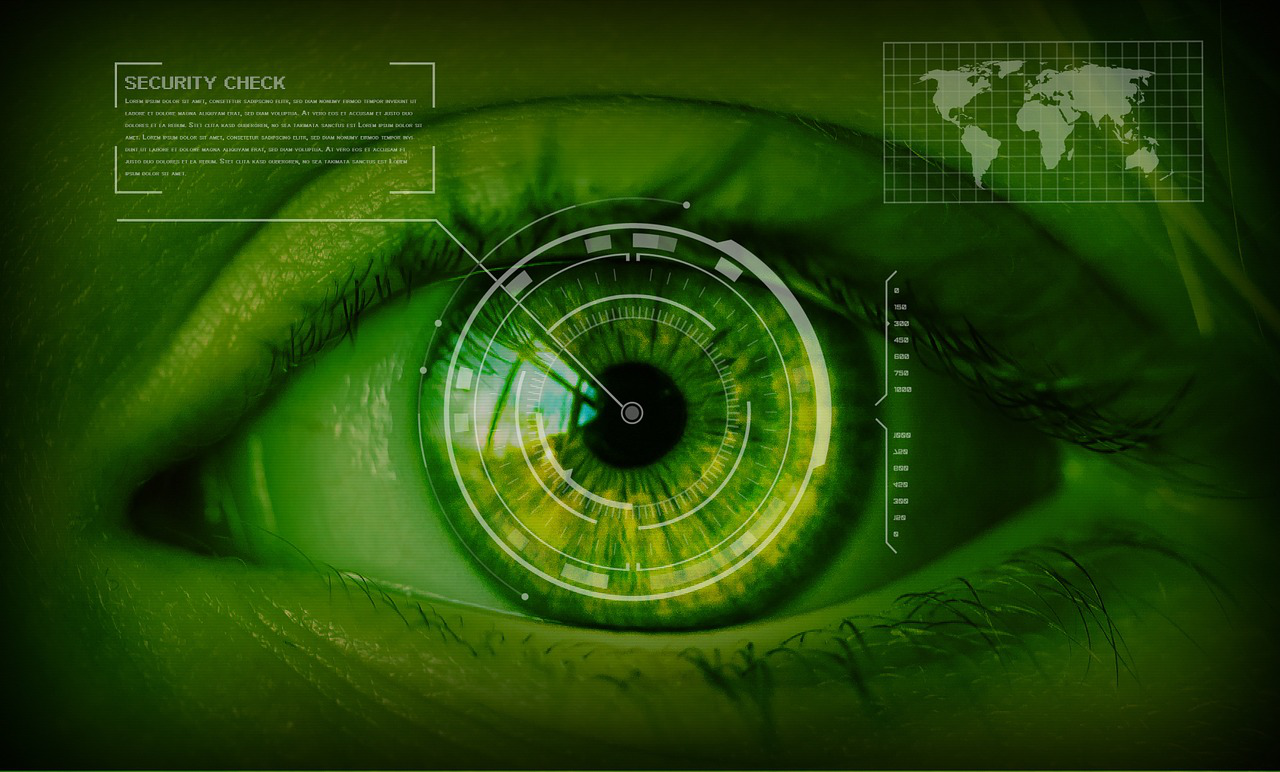

Iris recognition - Palm vein: It is one of the most secure biometrics and is the world’s first contactless personal identification system. It captures the vein pattern image of an individual while radiating it with near-infrared rays and can detect the vein pattern on the human palm with precision. The sensor emits infrared ray towards the palm of the hand and the blood flowing through these back to the heart with reduced oxygen absorbs the radiation and causes the veins to appear as a black pattern. This pattern is then recorded and stored in an encrypted format in a database, as a reference for future comparison. Each time a person wants to log in by using his palm, the newly captured image is processed and then compared to the stored one for verification. The number and positions of veins, along with their crossing points are compared and depending on the verification results the person is either granted or denied access.

Palm vein recognition - Voice identification systems: It validates an individual’s identity by using certain characteristics extracted from his/her voice. Voice recognition, referred to a voiceprint, is the identification and authentication factor of the vocal modalities. By measuring the sounds a user makes while speaking, voice recognition software can measure the unique biological factors that produce her voice. Voiceprints can be measured passively as a user speaks naturally in conversation, or actively, if he/she is made to speak a passphrase. The key is that true voice recognition measures the minutia of the voice, and is not wholly dependent on a spoken code or passphrase.
Advantages
- Ease of Use
- Security and Accuracy
- Cannot be forgotten or lost
- Return on Investment
- Safer compared to other Security methods
- Biometrics reduces administrative costs
Disadvantages
- Environment and usage can affect measurements
- Systems are not 100% accurate
- Require integration and/or additional hardware
- Cannot be reset once compromised
- Spoofing the fingerprint
- Hacking the Biometric software
Technology penetrates every possible aspect of our personal and social life and the demand of this application and device is set to increase. Many service providers have already integrated Smartphone applications with built-in biometric hardware for customer authentication to access services. Fingerprint sensor is the most common biometrics hardware used on most Smart phones. Devices like Samsung Galaxy S8 have already integrated iris recognition and Apple’s iPhone X’s face biometrics have already paved the way for other biometric modalities to grow.

References:
https://heimdalsecurity.com/blog/biometric-authentication/
https://www.bayometric.com/global-biometric-market-analysis/
https://findbiometrics.com/solutions/voice-speech-recognition/
